1. Abxixic Acid (Acid Abscisic) What is it ? Origin Abxixic Acid (Acid Abscisic).
– Acid Abscisic, also known as Dormin, Dormic Acid (DMA), is a group of natural and man-made substances considered as a plant hormone – a growth inhibitor.
In 1961, two American scientists, Liu and Carn, isolated a substance in the form of crystals from the old cotton fruit and when treated for young leaflets caused the fall and called the substance Abscisic I.
In 1963, Chkuma and Eddicott extracted a substance from the old bean tree leaves and named it Abscisic II. At this time, Wareing and his colleagues also isolated an inhibitor in the dormant shoots and named it “Dont”. In 1966, polarized spectroscopy determined the chemical nature of the inhibitor.
In 1967, the International Conference on Growth Regulators in Ottawa named the growth inhibitor Abscisic Acid (ABA) as the chemical formula C15H20O4.
2. Abxixic acid formula (Acid Abscisic)

Abxixic Acid (Acid Abscisic)
3. The biological effect of Abxixic Acid (Acid Abscisic)
– Abxixic acid (Acid Abscisic) inhibits growth
ABA inhibits nucleic acid synthesis in the cell, inhibiting protein synthesis, thereby affecting plant growth, aging and shortening life cycles.
– Abxixic Acid Abscisic regulates the loss of appetite
ABA stimulates the formation of the knockout floor causing the fall. When there is an agent that induces a loss of temperature such as too high or too low temperature, waterlogging, drought, pestilent insects …, the ABA content in leaves and fruits increases rapidly resulting in their loss. Therefore, in old decaying parts containing ABA.
– Abxixic acid (Acid Abscisic) regulates sleep
In the dormant body, the ABA content increased by 10 times that of the nutrient regimen, inhibiting germination. Sleeping rests until the ABA levels are reduced to a minimum.
Measures to reduce ABA or ABA antagonists such as GA are capable of breaking down sleep, stimulating germination. For example, cold storage and preservation have a very rapid reduction in ABA (70% seed and 30% fruit and tubers), and tubers can germinate when sown.
– Abxixic acid (Acid Abscisic) regulates the closure of the stomata
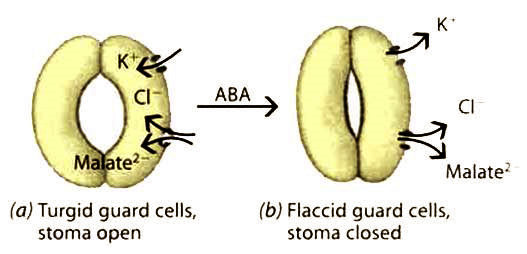
One of the mechanisms that regulate the opening and closing of the stomatitis is the hormone mechanism. As the ABA levels increase in the leaves, the stomata close to limit the escape of water vapor.
Exogenous ABA treatment for stomatal leaves closes rapidly, thus reducing leaf transpiration. The function of controlling stomatal openings is related to the rapid mobilization of K + ions. ABA causes the cell to build up causing the K + hole, loss of ductility and stomata closing. Exogenous ABA treatment closes the stomata to limit evapotranspiration, reducing leaf dehydration.
Acid Abscisic is considered a stress hormone.
When plants encounter environmental environmental inconsistencies, the ABA levels increase rapidly in the tree, helping the plant to undergo temporarily unfavorable conditions. For example, when drought occurs, the ABA content in the leaves increases, the stomata close and the trees avoid dehydration.
– Abxixic acid (Acid Abscisic) is the old hormone
The degree of aging of the organ and of the plant is associated with the accumulation of ABA in them. When the reproductive organs and reserves are formed, ABA is synthesized and accumulates the most and the rate of aging also increases.
4. Application of Abxixic Acid (Acid Abscisic)
Growth retardants are synthetic synthetic agents that act as growth inhibitors but do not alter reproductive traits. Used to make trees, trees, tires, etc.
– The herbicide destroys the TB films and biofilms, inhibits photosynthesis, disrupts the growth process, halts the process of cell division, inhibits its biosynthesis, and other plants. not harmed.-
– Antitranspirant – causes the stomatitis to shut down, reducing the escape of water vapor to avoid dehydration.
– inhibits ripening of fruit
– Application of sleep (resting) seeds by inhibiting cell growth – inhibiting seed germination.
– Reduces the production of enzymes needed for photosynthesis.




 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt




